Accessing IMU Data on Nicla Vision
Learn how to access the data from the accelerometer and gyroscope that comes with the LSM6DSOXTR IMU module.
Overview
In this tutorial, you will learn how to access the gyroscope and accelerometer that are placed on the Nicla Vision board. For this, you will be using the Arduino_LSM6DSOX library and the Arduino IDE, printing the values in the Serial Monitor of the Arduino IDE.
Goals
The goals of this project are:
- Read accelerometer data
- Read gyroscope data
- Print the data in the Serial Monitor
Hardware & Software Needed
- Arduino IDE (online or offline).
- LSM6DSOX library
- Nicla Vision
IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit)
An IMU is a component that consists of different sensors and can record data such as specific force, angular rate, orientation. The Nicla Visions IMU has a gyroscope and a accelerometer. On the image below you can see exactly where the IMU is located on the board.
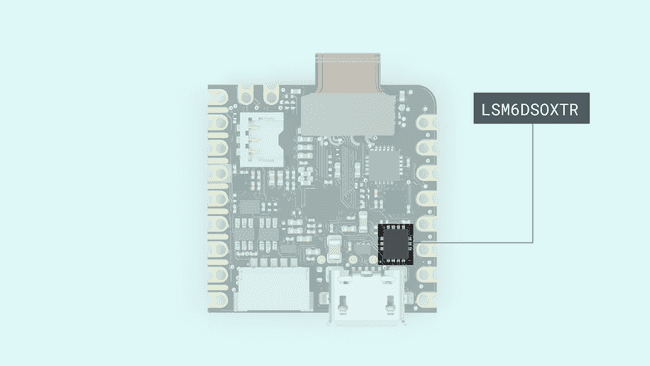
Accelerometer & Gyroscope
An accelerometer is an electromechanical device used to measure acceleration forces. Such forces may be static, like the continuous force of gravity, or, as in the case of many mobile devices, dynamic to sense movement or vibrations.
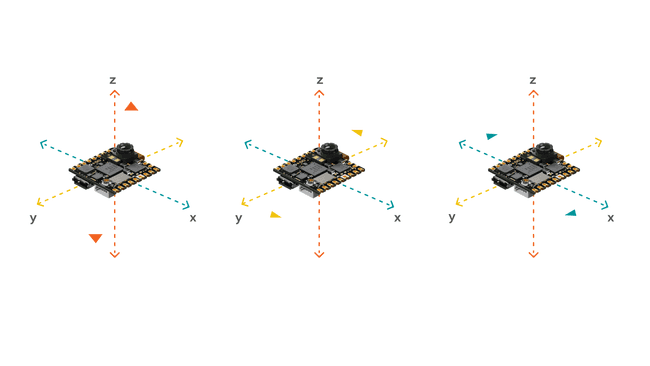
A gyroscope sensor is a device that can measure and maintain the orientation and angular velocity of an object. Gyroscopes are more advanced than accelerometers, since they can measure the tilt and lateral orientation of an object, whereas an accelerometer can only measure its linear motion. Gyroscope sensors are also called "Angular Rate Sensors" or "Angular Velocity Sensors". Measured in degrees per second, angular velocity is the change in the rotational angle of the object per unit of time.
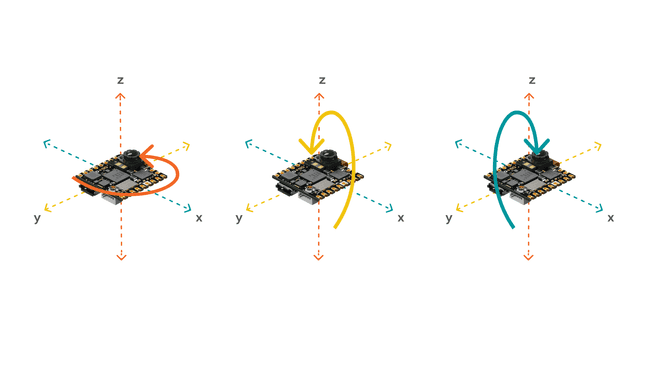
In this tutorial, you will use the gyroscope as an indicator for the direction of the force that is applied to the board. You will also use the accelerometer as a "level" that will provide information about the position of the board. With this application you will be able to read what the relative position of the board is as well as its orientation, by tilting the board up, down, left or right. The results will be visible through the Serial Monitor.
Instructions
Setting up the Arduino IDE
Make sure the latest Nicla Core is installed in the Arduino IDE. Tools > Board > Board Manager.... Here you need to look for the Arduino Mbed OS Nicla Boards and install it. Now you have to install the library needed for the IMU. Go to Tools > Manage libraries.., search for Arduino_LSM6DSOX and install it.
IMU Sketch
The full sketch can be found at the end of the Instructions section. Upload the sketch to the board.
To use the IMU you first need to include the library. To simplify the values coming from the IMU, you can create a variable for each axis.
1#include <Arduino_LSM6DSOX.h>2
3float Ax, Ay, Az;4float Gx, Gy, Gz;To initializes the library you need to call
IMU.begin()IMU.accelerationSampleRate()IMU.gyroscopeSampleRate()1void setup() {2 Serial.begin(9600);3
4 while(!Serial);5
6 if (!IMU.begin()) {7 Serial.println("Failed to initialize IMU!");8 while (1);9 }10 11 Serial.print("Accelerometer sample rate = ");12 Serial.print(IMU.accelerationSampleRate());13 Serial.println("Hz");14 Serial.println();15
16 Serial.print("Gyroscope sample rate = "); 17 Serial.print(IMU.gyroscopeSampleRate());18 Serial.println("Hz");19 Serial.println();20
21}In the loop of the sketch you can check the sensors to see if there is data available on the IMU sensors, using
IMU.accelerationAvailable()IMU.gyroscopeAvailable()IMU.readAcceleration(Ax, Ay, Az)AxAyAzdelay(500)1void loop() {2
3 if (IMU.accelerationAvailable()) {4 IMU.readAcceleration(Ax, Ay, Az);5
6 Serial.println("Accelerometer data: ");7 Serial.print(Ax);8 Serial.print('\t');9 Serial.print(Ay);10 Serial.print('\t');11 Serial.println(Az);12 Serial.println();13 }14
15 if (IMU.gyroscopeAvailable()) {16 IMU.readGyroscope(Gx, Gy, Gz);17 18 Serial.println("Gyroscope data: ");19 Serial.print(Gx);20 Serial.print('\t');21 Serial.print(Gy);22 Serial.print('\t');23 Serial.println(Gz);24 Serial.println();25 }26
27delay(500);28
29}Testing It Out
After successfully uploading the code to the board, you will need to open the Serial Monitor to initialize the program. Once you open it, data will start printing.
Complete Sketch
1#include <Arduino_LSM6DSOX.h>2
3float Ax, Ay, Az;4float Gx, Gy, Gz;5
6void setup() {7 Serial.begin(9600);8
9 while(!Serial);10
11 if (!IMU.begin()) {12 Serial.println("Failed to initialize IMU!");13 while (1);14 }15 16 Serial.print("Accelerometer sample rate = ");17 Serial.print(IMU.accelerationSampleRate());18 Serial.println("Hz");19 Serial.println();20
21 Serial.print("Gyroscope sample rate = "); 22 Serial.print(IMU.gyroscopeSampleRate());23 Serial.println("Hz");24 Serial.println();25
26}27
28void loop() {29
30 if (IMU.accelerationAvailable()) {31 IMU.readAcceleration(Ax, Ay, Az);32
33 Serial.println("Accelerometer data: ");34 Serial.print(Ax);35 Serial.print('\t');36 Serial.print(Ay);37 Serial.print('\t');38 Serial.println(Az);39 Serial.println();40 }41
42 if (IMU.gyroscopeAvailable()) {43 IMU.readGyroscope(Gx, Gy, Gz);44 45 Serial.println("Gyroscope data: ");46 Serial.print(Gx);47 Serial.print('\t');48 Serial.print(Gy);49 Serial.print('\t');50 Serial.println(Gz);51 Serial.println();52 }53
54delay(500);55
56}Conclusion
In this tutorial you have learned how to use the Arduino_LSM6DSOX library to access the IMU on the Nicla Vision. With this you learned how to print the gyroscope and accelerometer data in the Arduino IDE Serial Monitor.
Suggest changes
The content on docs.arduino.cc is facilitated through a public GitHub repository. If you see anything wrong, you can edit this page here.
License
The Arduino documentation is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 license.